Technical specifications - for the government using other methods
This text describes how to connect a Sender System with a Fina system for sending invoices from a Sender to a Recipient (users of the government budget). It is intended for all interested parties that will participate in the implementation of the solutions on the Sender side.
This text describes all messages exchanged by systems, means of exchange, as well as levels of security, e.g., protection of transmissions.
Data will be exchanged using XML messages via the SOAP web service. This kind of data exchange does not depend on the technology used on the Sender side, or on Fina as an information intermediary, or on the part of budget users such as the final Recipient.
Definitions and abbreviations
| SSL | Secure Sockets Layer - a protocol that protects the communication channel |
| EV | Extended Validation - The process of checking a business entity when issuing an SSL certificate |
| Sender | Sender of invoice to government budget user |
| Recipient | Government budget user |
| ERP | Enterprise Resource Planning – Business system on the Sender’s end |
| SOAP | Simple Object Access Protocol - Protocol used to exchange data between two web service systems |
Integrity protection
Integrity protection is achieved through process controls on the Sender side. The sender must be able to determine the origin of the invoice and the completeness of the content through internal process controls.
Communication conditions
Data exchange in the e-Invoice system for the government between Fina and a Sender is done through the Internet. Sending invoices via web services implies the fully automated sending of invoice from an ERP Sender system to a Recipient system through the Fina e-Invoice system for the government.
For this type of automated invoice sending, the Sender must do the following:
- establish process controls to be able to prove the origin of the invoice, or who issued the invoice, and process controls to prove the completeness of the content,
- must possess an SSL certificate from a trusted issuer which needs to have the exact and verified name of the business entity who issued it and meet the requirements set out in the "Baseline Requirements Certificate Policy for Issuance and Management of Publicly-Trusted Certificates" that is issued by the CA/Browser Forum, or higher level requirements (such as requirements for EV certification). The User may also request a Fina Server SSL certificate to establish a secure connection between their own ERP and the Fina e-Invoice system for the government,
- adjust the ERP to create and send a SOAP message.
Web service
For its part, Fina has created a web service for receiving data via a standardized XML schema.
Documents that can be sent through the e-Invoice web service system for the government are:
- Invoice (with accompanying documentation attached),
- Approval (with accompanying documentation attached).
All messages sent through the web service have the same basic layout. It consists of headers (HeaderSupplier) and Data.
Information (data) is defined for each message separately and differ within the element of the XML structure depending on the message. Messages that contain standalone XML structures (such as xml e-invoices) are embedded in a "envelope" (e.g., InvoiceEnvelope) of the base64binary type that contains the original XML encoded in Base64.
Basic settings concept:
- Fina has created a web service with methods for sending outgoing e-invoice and e-approval (SendB2GOutgoingInvoice) messages, and methods for sending a message to retrieve the status of the outgoing invoice and trial run, echo message,
- when a web service is called, Fina will establish an SSL connection with client authentication (2-way SSL)
- prior to using the Fina e-Invoice for the government, process controls on the Sender's side must be established for proving the origin of invoices and the completeness of their content,
- for each SOAP message there will be a SOAP acknowledgment message.
Sending Echo message
Sending outgoing invoice
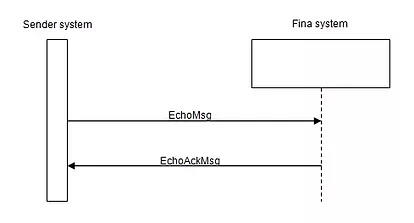
Checking web service function (Echo method)
The Sender creates an echo SOAP message to test for web service availability. Fina synchronously answers with a reply message.
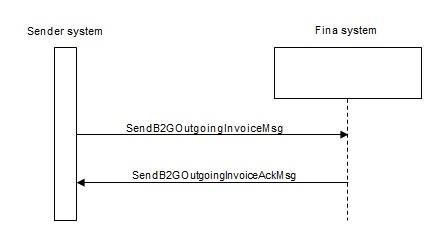
If the echo message has successfully been sent and Fina has responded by a reply message, the sender creates a SOAP message for sending the outgoing invoice or approval and calls the web service on the Fina side. Fina synchronously replies with a message on the results of processing.
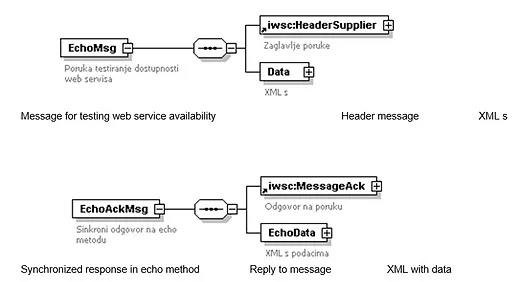
Elements of EchoMsg messages
- HeaderSupplier
- MessageID - Unique message number
- SupplierID - Issuer identifier (OIB) - (9934:12345678909)
- AdditionalSupplierID - Additional Issuer Identifier (GLN, JUS, ...) - 0088:38545468711
- MessageType - Message type: 9999 - echo message
- MessageAttributes - Message attributes
- Data
- EchoData
- Echo - Text content
- EchoData
Elements of EchoAckMsg messages
- MessageAck
- MessageID - Unique message number
- MessageAckID - Unique message number to which the reply is addressed
- MessageType - 10000 - Reply to echo message
- AckStatus - Reply status
- AckStatusCode - System status code
- AckStatusText - System status description
- EchoData
- Echo - Text content
Sending an Echo and Echo confirmation message
Method for sending outgoing messages (invoice, approval)
After successfully sending echo SOAP messages, the sender creates a SOAP message to send the document:
Elements of SendB2GOutgoingInvoiceMsg messages (SendB2GOutgoingInvoice method):
- HeaderSupplier
- MessageID - Unique message number
- SupplierID - Issuer identifier (OIB) - (9934:12345678909)
- AdditionalSupplierID - Additional issuer identifier (GLN, JUS,...) - 0088:38545468711
- MessageType - Message type: 9001 - Sending outgoing invoice
- MessageAttributes - Message attributes
- Data
- B2GOutgoingInvoiceEnvelope
- XMLStandard - Standard XML document (UBL or CII)
- SpecificationIdentifier – Customized XML document (fixed - urn:cen.eu:en16931:2017)
- SupplierInvoiceID - Invoice identifier in sender system
- BuyerID – Invoice recipient identifier in the system (OIB) - (9934:12345678909)
- AdditionalBuyerID - Additional invoice recipient identifier in system (GLN, JUS, ...) - (0088:38545468711)
- InvoiceEnvelope – Envelope of e-Invoice according to UBL schema
- CreditNoteEnvelope - Envelope of e-Approval according to UBL schema
- B2GOutgoingInvoiceEnvelope
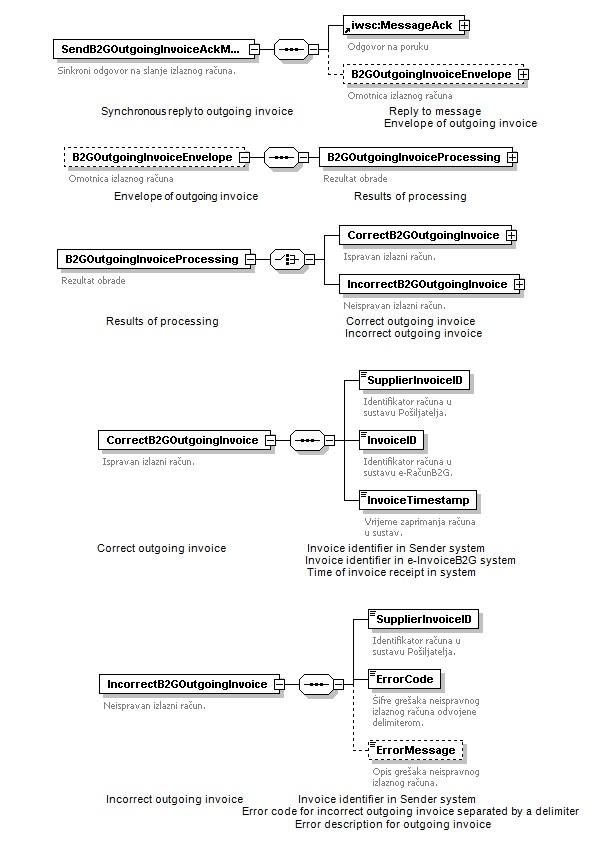
Elements of SendB2GOutgoingInvoiceAckMsg messages:
- MessageAck
- MessageID - Unique message number
- MessageAckID - Unique message number to which the reply relates
- MessageType - Message type: 9002 - Synchronous reply to SendB2GOutgoingInvoiceMsg
- AckStatus - reply status
- ACCEPTED or
- MSG_NOT_VALID or
- SYSTEM_ERROR
- AckStatusCode - System status code
- AckStatusText – (optional) – System status description
- B2GoutgoingInvoiceEnvelope
- CorrectB2GOutgoingInvoice - Correct outbound invoice
- SupplierInvoiceID - Invoice identifier in sender system
- InvoiceID - Invoice Identifier in B2G e-Invoice
- InvoiceTimestamp - Time of receiving invoices in the system
- IncorrectB2GOutgoingInvoice
- SupplierInvoiceID - Invoice identifier in sender system.
- ErrorCode – Error code of invalid outbound invoice separated by delimiter.
- ErrorMessage – Error description of incorrect outbound invoice.
- CorrectB2GOutgoingInvoice - Correct outbound invoice
A reply message consists of two parts:
- MessageAck
- B2GOutgoingInvoiceEnvelope
The MessageAck section contains basic information about the SOAP message itself, while in the B2GOutgoingInvoiceEnvelope section is found the processing data of the invoice that was sent.
Message Status
| AckStatus | AckStatusCode | AckStatusText |
| ACCEPTED | 10 | Message Received |
| MSG_NOT_VALID | 90 | XML message is not correct |
| MSG_NOT_VALID | 91 | Incorrect message signature |
| SYSTEM_ERROR | 99 | System error on the web service end + description |
If the SOAP message is consistent with the web service definition (wsdl) then the Message Accept / AckStatus element always displays the ACCEPTED reply regardless of whether the data itself, e.g. the invoice, is correct. If the SOAP message is not in accordance with the definition, MSG_NOT_VALID will appear in the response. The SYSTEM_ERROR value shows that there are major system issues (e.g., a runtime exception) and an indication that user support should be notified to verify the reason.
The B2GOutgoingInvoiceEnvelope section contains data on a processed document (invoice, approval...), and the entire element appears only if MessageAck / AckStatus ACCEPTED. If AckStatus is MSG_NOT_VALID or SYSTEM_ERROR then the B2GOutgoingInvoiceEnvelope element does not appear in the reply message.
If the UBL document is correct, then the CorrectB2GOutgoingInvoice element appears with the invoice identifier data from the sender's system (invoice number), the invoice identifier under which it was sent via the e-Invoice system and the timestamp of receipt appears.
If the UBL document is incorrect, then the IncorrectB2GOutgoingInvoice element appears with the invoice identifier data from the sender's system (invoice number), an error code, and description appears (separated by a delimiter if there are multiple errors). In this case, it is necessary to correct the errors and send the message back through the system.
Systems for sending confirmation reply messages
Method for retrieving outgoing invoice status
This method is used to check the status of a specific outgoing invoice. The invoice number from the sender's system and the year of issue of the invoice are used as identifiers.
Elements of GetB2GOutgoingInvoiceStatusMsg messages (method GetB2GOutgoingInvoiceStatus):
- HeaderSupplier
- MessageID - Unique message number
- SupplierID - Issuer identifier (OIB) - (9934:12345678909)
- AdditionalSupplierID - Additional issuer identifier (GLN, JUS, ...) - 0088:38545468711
- MessageType - Message Type: 9011 – Retrieval status of outbound invoice
- MessageAttributes - Message attributes
- Data
- B2GOutgoingInvoiceStatus
- SupplierInvoiceID - Invoice identifier in sender system
- InvoiceYear - The year of the invoice in the sender's system
- DocumentCurrencyCode - true/false currency print of the partially paid invoice amount in the acknowledgment message (optional element)
- B2GOutgoingInvoiceStatus
Elements GetB2GOutgoingInvoiceStatusAckMsg Message:
- MessageAck
- MessageID - Unique message number
- MessageAckID - Unique message number to which the reply is addressed
- MessageType - Message Type: 9012 - Synchronous Response to GetB2GOutgoingInvoiceStatusMsg
- AckStatus - Reply status
- ACCEPTED or
- MSG_NOT_VALID or
- SYSTEM_ERROR
- AckStatusCode - System status code
- AckStatusText – (optional) – System status description
- B2GOutgoingInvoiceStatus
- SupplierID - Invoice sender identifier in the e-Invoice system
- AdditionalSupplierID - Additional issuer identifier (GLN, JUS, ...) - 0088:38545468711
- InvoiceID - Invoice identifier in e-Invoice system
- SupplierInvoiceID - Invoice identifier in the sender system
- InvoiceTimestamp - Timestamp of invoice in the e-Invoice B2G system
- DocumentStatus – System status of e-Invoice
- StatusCode - Status code in e-Invoice system
- StatusText - Description of status codes in e-Invoice system
- StatusTimestamp - Timestamp status in the B2G e-Invoice system
- Note - Status note (e.g., reason for rejection)
- PartialAmount - Amount of partially paid invoice
- DocumentCurrencyCode - Currency of the partially paid invoice amount (optional element)
Messages and web service definition
Messaging and web services definition (WSDL) schema can be seen here.
UBL schema
The UBL schema can be downloaded from the Oasis site:
Invoice: https://docs.oasis-open.org/ubl/os-UBL-2.1/xsd/maindoc/UBL-Invoice-2.1.xsd
Credit Note: https://docs.oasis-open.org/ubl/os-UBL-2.1/xsd/maindoc/UBL-CreditNote-2.1.xsd
Common Schema (all are needed): https://docs.oasis-open.org/ubl/os-UBL-2.1/xsd/common/
Types and descriptions of messages exchanged
The table below describes the types of messages and replies:
| Message Type | Description | Message / methods |
| 9999 | Echo | EchoMsg |
| 10000 | Synchronous response to Echo | EchoAckMsg |
| 9001 | Sending an outgoing invoice | SendB2GOutgoingInvoiceMsg |
| 9002 | Synchronous response to sending of outgoing invoice | SendB2GOutgoingInvoiceAckMsg |
| 9011 | Outgoing invoice receiving status | GetB2GOutgoingInvoiceStatusMsg |
| 9012 | Synchronous response to receiving status of an outgoing invoice | GetB2GOutgoingInvoiceStatusAckMsg |
Procedures before production
Prior to launching on the production system, it is necessary to verify the successful exchange of data on Fina and Sender test environments.
No exceptions can be made for a lack of exchange testing, on the test environments of Fina and Sender. Likewise, it is necessary to document the data exchange components in detail.